Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that is caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus.
The infection causes small, raised, and usually painless bumps on the skin. The bumps are typically pearl-like in appearance and can occur anywhere on the body.
Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children, but it can also occur in adults.
In this article, we will discuss the definition, types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum Types:
There are four types of molluscum contagiosum, which are classified based on the location of the infection:
Molluscum contagiosum of the face:
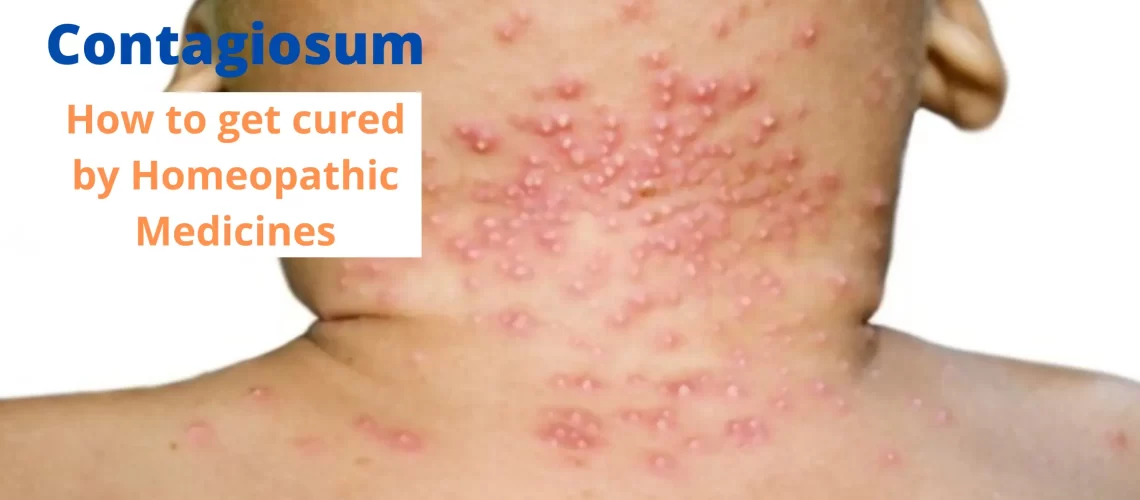
This type of molluscum contagiosum occurs on the face, neck, and eyelids.
Molluscum contagiosum of the trunk:
This type of molluscum contagiosum occurs on the trunk, including the chest and back.
Molluscum contagiosum of the limbs:
This type of molluscum contagiosum occurs on the arms and legs.
Molluscum contagiosum of the genital area:
This type of molluscum contagiosum occurs in the genital area and is sexually transmitted.
Molluscum contagiosum Causes:
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, which is a member of the poxvirus family.
The virus can also be spread through sexual contact, making the genital area a common site for infection in adults.
The virus is a highly contagious virus that can spread from person to person through direct skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated objects, such as towels, clothing, or toys.
The virus can also be transmitted through sexual contact in sexually active individuals, leading to molluscum contagiosum lesions in the genital or pubic area.
Molluscum contagiosum is most commonly seen in children, but it can affect individuals of all ages, including adults.
The virus enters the skin through small breaks in the skin barrier, such as cuts, abrasions, or insect bites, and infects the skin cells, leading to the development of characteristic lesions.
Molluscum contagiosum Symptoms:
Signs –
One of the key signs of molluscum contagiosum is the central umbilication or depression in the middle of the lesion, which gives it a characteristic “dimpled” appearance.
This central umbilication may contain a white, waxy, or cheesy material that can be expressed when squeezed.
Another hallmark sign of molluscum contagiosum is the self-limiting nature of the infection.
The lesions typically resolve spontaneously over time, usually within 6 to 12 months, although they can persist for longer in some cases.
Molluscum contagiosum lesions can occur on any part of the body, but they are commonly found on the face, neck, arms, hands, and genital area.
In sexually active adults, molluscum contagiosum lesions may also be found in the genital or pubic area, and they may be sexually transmitted through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated objects.
Symptoms –
The symptoms of molluscum contagiosum include:
Small, raised, and usually painless bumps on the skin. The bumps are typically pearl-like in appearance and can occur anywhere on the body.
The eruptions may be itchy or sore, but they are usually not painful.
The eruptions may have a central dimple or core. The eruptions may be red, pink, or flesh-colored. The eruptions may occur in clusters or groups.
The bumps may spread to other parts of the body through scratching or rubbing.
Small, round, flesh-colored, or pinkish bumps are usually painless and can vary in size from 2-5 millimeters in diameter. They may have a central indentation or waxy appearance.
Dome-shaped lesions with a pearly or shiny appearance may have a shiny or pearly appearance and can be dome-shaped.
The central dimple or plug may have a central dimple or plug, which is often filled with a white, cheesy material.
Itching or tenderness is one of the main symptoms. While molluscum contagiosum is generally painless, some people may experience mild itching or tenderness around the affected areas.
The spread of bumps is rapid. The bumps may spread to nearby skin through scratching, friction, or contact with contaminated objects, such as towels or clothing.
Inflammation or redness shows an ongoing infection. Occasionally, the bumps may become inflamed or red, especially if they are scratched or irritated.
Molluscum contagiosum bumps can be unsightly and may cause discomfort or embarrassment, particularly if they appear on visible areas of the body, such as the face, neck, or genitals.
It’s important to note that molluscum contagiosum is usually a benign condition and is not usually associated with other symptoms or systemic illness.
However, it can be contagious and may spread to other parts of the body or other individuals through skin-to-skin contact or sharing contaminated objects.
If you suspect you have molluscum contagiosum, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Risk Factors for Molluscum contagiosum :
There are several risk factors for developing molluscum contagiosum, including:
Age: Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children, particularly those under the age of 10. This may be because children are more likely to come into close contact with each other and share toys, clothing, and other items.
Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or who are taking immunosuppressant medications, are at a higher risk of developing molluscum contagiosum.
Close contact with infected individuals: The virus that causes molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals or through contact with contaminated objects, such as towels or toys.
Participation in certain activities: People who participate in certain activities, such as contact sports or swimming, may be at a higher risk of developing molluscum contagiosum due to close physical contact with others.
Poor hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands or sharing personal items, can increase the risk of contracting molluscum contagiosum.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop molluscum contagiosum.
Taking steps to prevent the spread of the virus, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, can help reduce the risk of infection.
Diagnosis for Molluscum contagiosum :
Molluscum contagiosum can usually be diagnosed through a physical exam by a healthcare provider.
Here are some of the diagnostic methods used to confirm molluscum contagiosum:
Visual exam:
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose molluscum contagiosum by examining the skin lesions.
Molluscum contagiosum typically appears as small, raised, round, and flesh-colored bumps with a central indentation or white core.
Biopsy:
In some cases, a healthcare provider may perform a biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of the affected skin tissue for analysis under a microscope.
This can help confirm the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum and rule out other conditions.
Scraping:
In some cases, a healthcare provider may scrape the surface of the lesion to collect a sample for examination under a microscope. This can help confirm the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum.
Dermoscopy:
Dermoscopy is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses a specialized microscope to examine skin lesions.
It can help healthcare providers distinguish between different types of skin lesions and confirm the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum.
It’s important to seek medical advice if you suspect you have molluscum contagiosum or any other skin condition, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of the infection and minimize complications.
Molluscum contagiosum Management:
Molluscum contagiosum often goes away on its own without treatment, but treatment can help speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Here are some common treatment options for molluscum contagiosum.
Wait and watch: In many cases, molluscum contagiosum will resolve on its own within 6-12 months without any treatment.
This is often the recommended course of action for mild or asymptomatic cases.
Physical removal:
Healthcare providers may use a variety of methods to physically remove the lesions, such as freezing them with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy), scraping them off with a sharp instrument (curettage), or using a laser to remove them.
Topical medication:
Certain topical medications, such as imiquimod, can be applied directly to the lesions to stimulate the immune system and help the body fight off the virus.
Oral medication:
In some cases, oral medications, such as cimetidine, can be used to boost the immune system and help the body fight off the virus.
Home remedies:
Several home remedies may help soothe the skin and reduce itching, such as applying apple cider vinegar, tea tree oil, or coconut oil to the affected area.
It’s important to note that some treatments, such as physical removal, may cause scarring or other complications.
It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of each treatment option with a healthcare provider before proceeding.
Additionally, it’s important to avoid picking or scratching the lesions, as this can increase the risk of spreading the infection to other parts of the body or other people.
Best Homeopathic Medicines for Molluscum contagiosum:
Homeopathy is an alternative system of medicine and when it comes to skin conditions, homeopathy is believed to work by addressing the underlying imbalances in the body that may be contributing to the skin condition, rather than simply treating the symptoms on the surface of the skin.
Homeopathic remedies for skin conditions are chosen based on the individual’s unique symptoms, medical history, and constitutional characteristics, as well as the specific characteristics of the skin condition.
Some important remedies for Molluscum contagiosum are as follows –
Alumina
Anacardium Orientale
Antimonium crudum
Argentum nitricum
Bovista
Calcarea sulphuricum
Dulcamara
Hepar sulphuris calcareum
Lachesis
Mercurius solubilis
Mezereum
Natrum muraticum
Nitric acid
Phosphorus
Rhus Toxicodendron
Sepia
Silicea
Staphysagria
Sulphur
Thuja occidentalis
1. Alumina – rashes with dry skin.
Pain on touching the eruptions. There is dry, chapped skin associated with molluscum.
There is intolerable itching in the hot summer.
The eruptions become dry and cracked.
Thirstlessness with fever
Dose and potency: 12 CH potency, 4 pills two times a day, and mother tincture can be taken 15 drops in half glass water once a day.
2. Anacardium orientale – eruptions of palms.
The patient is very irritable and has a fever.
Skin itching is better by cold water applications.
molluscum of hands and palms
Dose and potency: 30 CH potency is repeated every 5 hours once a day.
3. Antimonium crudum: Molluscum of people who are prone to friction or pressure.
Eruptions on hands appear fleshy and red.
A circle of ulcers surrounds the eruptions and causes stinging pain.
Especially suited for individuals who tend to grow fat.
Molluscum virus also affects the neck and the arms.
Dose and potency: 200 CH potency, 6 pellets two times a day can be repeated.
4. Argentum nitricum: eruptions turn brown.
This remedy is often recommended for an eruption that causes ulceration.
It is best suited for patients with anxiety about health and digestive symptoms.
Dose and potency: 30 CH potency, 6 pellets three times a day can be repeated according to the frequency of the symptoms.
5. Baryta carbonica: eruptions on hands and fingers
This remedy is often recommended for dwarfs with a tendency for enlargement of glands and indurations.
Eruptions appear on the hands and fingers.
Dose and potency: 12 CH potency, 6 pellets three times a day can be repeated according to the seriousness of the symptoms.
6. Bovista: skin eruptions with severe inflammation.
Skin eruptions become very inflamed and cause burning pain.
Awkwardness may accompany a fever.
Diarrhea before the onset of fever is also a characteristic symptom.
Dose and potency: 200 CH potency, 4 pellets two times a day can be repeated accordingly.
7. Calcarea carbonica: Skin eruptions are painful and inflamed.
This remedy may be suggested when the molluscum contagiosum lesions are hard, large, and slow to heal.
It may be recommended for individuals who are overweight or have a tendency towards coldness and clamminess.
Dose and potency: 12 CH twice a day until the pain subsides.
8. Calcarea sulphuricum: pus-filled lesions with yellow suppurations
Indicated for pus-filled lesions with yellow, thick discharge, and individuals with a history of suppuration or boils.
Dose and potency: 200 CH potency thrice a day
9.Dulcamara: Indicated for molluscum contagiosum
Eruptions are aggravated by cold, damp weather, or wet conditions.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
10. Hepar sulphuris calcareum: molluscum with abscess.
Indicated for painful, sensitive lesions prone to suppuration, and individuals who are sensitive to touch or cold air.
Dose and potency: : 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
11. Lachesis: aggravation from touch with burning.
It is a great remedy for left-sided eruptions of the body. The lymph nodes may be swollen.
Aggravation from the slightest touch and better from hard pressure.
Dose and potency: 12 CH potency- 4 pills, twice a day.
12. Mercurius solubilis: Inflammation of glands with suppuration.
Skin erupts dark and looks dirty.
Other associated symptoms may include offensive breath, and excessive salivation during sleep.
Dose and potency: 30 CH potency can be repeated every 6 hours
13. Mezereum: Indicated for clustered lesions with thick crusts and burning.
Molluscsum with intense itching sensations, and individuals sensitive to touch or cold air.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
14. Natrum muriaticum: Indicated for molluscum contagiosum around the eyes or mouth.
The complaints are associated with grief or emotional suppression.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
15. Nitric acid: Indicated for molluscum of mucous membranes. It is painful, bleeding lesions, or those prone to infection, and individuals who are irritable or exposed to chemicals.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
16. Phosphorus: Indicated for molluscum contagiosum with a tendency towards bleeding.
It is best suited for individuals who are tall, slender, and sensitive to light.
There is an intense thirst for cold drinks and feels better by rubbing.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
17. Rhus Toxicodendron: Indicated for red, swollen.
The lesions itch, very intensely, are worsened by cold, damp weather, or poison ivy exposure, and are restless individuals.
The tip of the tongue is red.
Patients are very restless and toss about in bed.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day.
18. Sepia: Indicated for molluscum contagiosum with brownish or yellowish lesions.
It is best suited for individuals who are irritable, fatigued, and have hormonal imbalances.
The patient feels better by exertion and thunderstorms.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times a day
19. Silicea: eruptions have a slow healing tendency
The remedy is indicated for hard, slow-healing lesions prone to suppuration or abscess formation, and individuals with weak immunity.
Patients have profuse perspiration of palms and soles.
They cannot tolerate cold weather and may suffer from severe constipation.
Dose and potency: 3 pellets, 3 times for 5 days.
20. Staphysagria: the appearance of skin eruptions from suppressed anger.
Ailments appear from suppressed anger and spread throughout the body.
A strong siesta aggravation is a confirmatory symptom of the remedy
Dose and potency: 30 CH potencies should be given twice a day.
21 . Sulphur: Indicated for burning, itching lesions that worsen with warmth
It is indicated for burning and itching lesions and individuals who are warm-blooded and have dry skin.
The patient has an aversion to bathing and a desire for sweets.
Dose and potency: 30 CH potency – 6 pills once a day for 3 days.
22. Thuja occidentalis: Indicated for large, cauliflower-like lesions with a central depression.
It is mainly indicated for cauliflower-like growth and eruptions which appear like a dome in the center.
The patients also have an intense desire for onions and garlic.
Dose and potency: 30 CH potency – 3 pellets twice a day.

1 thought on “Molluscum Contagiosum- Symptoms & Cure by Homeopathy”
Can you pls explain what you mean by 3 pellets? No dosage mentioned